Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
in Everett, WA
Patients with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing eye conditions as a complication of their disease. These conditions can lead to vision loss and blindness and include diabetic retinopathy, cataracts and glaucoma. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in the United States.
Diabetic eye conditions often develop without any noticeable loss of vision or pain, so significant damage may have occurred by the time patients notice any symptoms. For this reason, diabetic patients need to have their eyes examined at least once a year. Early detection of eye disease can help prevent permanent damage.
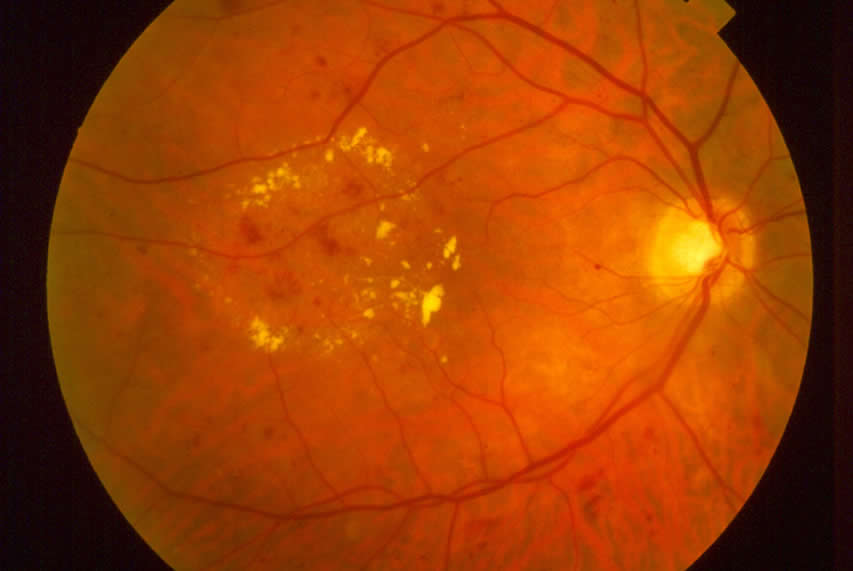
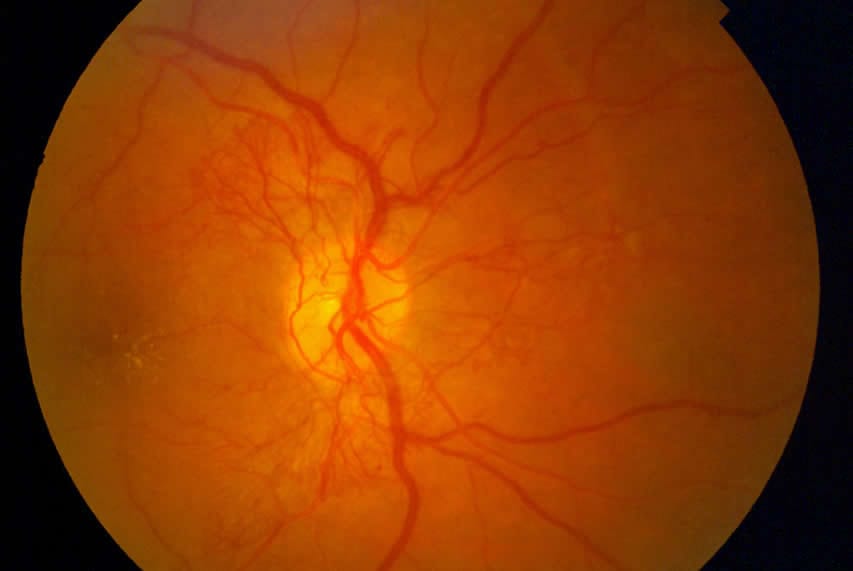
Diabetic-related eye problems develop from high blood sugar levels, which can cause damage to blood vessels in the eye. Over 40 percent of patients diagnosed with diabetes develop some form of eye disease as a result of their disease. The risk of developing eye problems can be reduced with regular eye exams and by controlling blood sugar levels with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic eye conditions develop in the retina as a result of microvascular abnormalities. The tiny blood vessels within the retina develop microaneurysms that, over time, leak blood. As new blood vessels develop to replace the blood vessels that are no longer viable, they also leak blood causing hemorrhages and permanent damage to the retina.
While diabetics struggle with a high sugar count in the blood along with insufficient insulin production, it is the lack of oxygen in the blood that leads to loss of vision.
Diagnosing Diabetic Eye Conditions
Diabetic eye conditions can be detected through a comprehensive eye exam. A comprehensive eye exam involves a visual acuity test to measure vision at various distances, and a dilated eye exam to examine the structures of the eye for any signs of disease. During this test, your doctor can examine the retina and optic nerve with a special magnifying lens. Tonometry may also be performed during a comprehensive eye exam to measure the pressure inside the eye with a special instrument.
Eye exams should be performed at least once a year or as soon as any potential problems are detected to ensure early detection of any serious conditions. Early detection is the strongest protection against diabetic eye diseases.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Options
Other than controlling blood pressure, blood cholesterol and the levels of blood sugar, treatment is not needed during the first three stages of diabetic retinopathy. In the fourth stage, proliferative retinopathy is treated with a laser surgery procedure known as scatter laser treatment. During the procedure the abnormal blood vessels are ablated causing them to shrink. This procedure works best once the blood vessels begin to bleed. Severe blood vessel bleeding may need to surgically corrected with a vitrectomy procedure to remove the blood from the eye.
Treatment for macular edema usually includes a laser procedure called focal laser treatment. During this procedure, several hundred small laser burns are placed in the areas of retinal leakage around the macula to prevent leakage from occurring and reduce the amount of fluid in the retina. This helps reduce the risk of vision loss and may improve lost vision in a small number of cases. Focal laser treatment is performed in your doctor’s office and can usually be completed in just one session.
There are several treatment types based on the condition of the patient’s eye, your Dr. will discuss options with you during your eye exam.
How to Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy can develop in anyone who has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The longer you have diabetes and the less controlled your blood sugar is, the more likely you are to develop diabetic retinopathy. You can’t always prevent it from developing, but early intervention and health management can help prevent severe vision loss. Here are some steps to take to reduce your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy:
- Manage your diabetes — Take your oral diabetes medications as directed. Eat a healthy diet and make a point of getting at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity, such as walking, each week.
- Monitor your blood sugar level — You may need to check your blood sugar level several times daily.
- Ask about a glycosylated hemoglobin test — This test, shortened to the hemoglobin A1C test, reflects your average blood sugar level for the two- to three-month period before the test. The A1C goal is to be under 7 percent.
- Control your blood pressure and cholesterol — A healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight loss may be enough, or you may need medication.
- Stop smoking — If you smoke, it increases your risk of diabetes complications, including retinopathy.
- Watch for vision changes — If you experience any sudden vision changes, or your vision becomes blurry, spotty, or hazy, call us at Physicians Eye Clinic immediately.
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy
As diabetes progresses, a person’s blood sugar levels rise. Too much sugar in the blood can lead to the blockage of the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina. This cuts off the blood supply. In response, the eye grows new blood vessels, but they don’t develop normally and can leak. There are two types of diabetic retinopathy:
- Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy — This is the more common form. New blood vessels aren’t growing. Instead the walls of the blood vessels in the retina weaken. Smaller vessels may develop bulges that can leak blood and other fluid into the retina. Larger vessels can become irregular in diameter. This early form of diabetic retinopathy can progress to the advanced form as more blood vessels become blocked.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy — In this more severe form of retinopathy, damaged blood vessels close off, instigating the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels in the retina. These can leak into the vitreous, the jelly-like filling of the center of the eye. Scar tissue will often form due to the new blood vessel growth, and this can cause the retina to detach from the back of the eye. The abnormal blood vessels may also interfere with the flow of fluid out of the eye, increasing pressure in the eyeball. This is glaucoma and the increased pressure can damage the optic nerve.
Is Scatter Laser Treatment Painful?
What Is The Recovery Time After a Scatter Laser Procedure?
These are outpatient procedures. You’ll need someone to drive you home from our offices, as we dilate your eyes to widen your pupils before the procedure. They will remain dilated for several hours, and you’ll need sunglasses to keep the bright light out of them while they remain dilated. Your vision may be blurry, and your eye may hurt a little for a day or two. Your vision should improve to its previous level in two to three weeks. The laser energy can damage some light-sensitive cells, particularly those with peripheral vision, to save more of the central vision. Laser photocoagulation will likely help prevent more severe vision loss over time.
What is Macular Edema?
Macular edema is the build-up of fluid in the macula, an area in the center of the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye and the macula is the part of the retina responsible for sharp, straight-ahead, central vision. Fluid buildup causes the macula to swell and thicken, and this distorts your vision.
What is Focal Laser Treatment?
Risks Of Focal Laser Treatments
The most common side effect with these laser procedures is the appearance of spots in your vision, typically just off to the side of your central vision. In most cases, these will go away, but in rare cases they persist. This is among the safest types of laser eye treatments. Focal laser treatment is not a cure, but it helps to stabilize the leakage that threatens vision loss. As your retinopathy progresses, You’ll likely need additional laser treatments in the future.
FAQs
What Are The Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Disease?
The early stages of diabetic eye disease do not have symptoms. As the condition worsens, however, it is common for symptoms such as floaters, blurry vision, dark areas in your vision, and, in the worst-case scenario, blindness.
Who Is At Risk for Diabetic Eye Disease?
Individuals who have Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes are at the highest risk of developing diabetic eye disease. It is important to note that the longer someone has uncontrolled diabetes, the higher their of developing eye complications is.
How Often Should I Have My Eyes Examined?
While the timeframe can vary from patient to patient, it is best to have your eyes examined at least once a year. However, your doctor will recommend the best treatment plan for you based on your diagnosis and symptoms.
Can Diabetic Eye Disease Cause Blindness?
Yes, if left untreated, diabetic eye disease can lead to severe vision loss and blindness. That is why early detection and treatment are necessary.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Diabetic Eye Disease?
In addition to a low-sugar, well-balanced diet, exercising regularly and not smoking can mitigate the risk and progression of the disease. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in leafy greens, fish, and whole grains can improve eye health. Also, reducing fine carbohydrate consumption is another important step in diabetes management. You should also schedule annual eye exams to help catch the disease faster.
Can Smoking Cause Diabetic Eye Disease?
Smoking does increase the risk and can accelerate the progression of diabetic eye disease.
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes With Regard to Eye Health?
Both types of diabetes can lead to diabetic eye disease. However, the risk may present earlier with individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
See What Our Patients Have To Say…
“Great surgery staff, they are so friendly and comforting. I am seeing better than I have in years.”
– KyserI have been a patient of Dr. Lueth’s for many years, and I am very pleased with his care. I recently underwent cataract surgery and appreciated the efficient and considerate care provided me. I would certainly recommend this group to anyone looking for excellent eye care. – Thomas H.